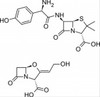
Amoxicillin:Potassium Clavulanate (2:1) is a combination of Amoxicillin (one part) and Potassium Clavulanate (Clavulanic Acid)(two parts) which prevents the degradation of Amoxicillin by β-lactamase enzymes and allows for greater efficacy against β-lactam resistant strains.
Amoxicillin is an extended-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic similar in structure to Ampicillin. Resistance to Amoxicillin is due to β-lactamase enzymes found in resistant strains.
Potassium Clavulanate, produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces clavuligerus, is a β-lactamase inhibitor which can irreversibly inactivate β-lactamase enzymes.
Amoxicillin:Potassium Clavulanate (2:1) is freely soluble in water.
We also offer:
| Mechanism of Action | Like all β-lactams, Amoxicillin targets PBP’s (penicillin binding proteins) involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised ultimately leading to the death of the cell. |
| Spectrum | Amoxicillin targets a wide range of β-lactamase negative Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including E. coli and a number of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species. Because peptidoglycan is synthesized in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, Amoxicillin can be used against a wide variety of microbes. Clavulanate competitively and irreversibly inhibits a wide variety of β-lactamases found in bacteria that are resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins. |
| Microbiology Applications | Amoxicillin is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Impurities | Single Impurity: ≤2.0% Total Impurities: ≤6.0% |
| References |
Ball AP, Geddes AM, Davey PG, Farrell ID, Brookes GR (1980) Clavulanic acid and Amoxycillin: A clinical, bacteriological, and pharmacological study. Lancet 1(8169):620-623 PMID 6102627 Fuchs PC, Barry AL, Thornsberry C, Gavan TL and Jones RN (1983) In vitro evaluation of augmentin by broth microdilutiona and disk diffusion susceptibility testing: Regression analysis, tentative interpretive criteria, and quality control limits. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24(1):31-38 PMID 6625554 Kim SH et al (2015) Characterization of Amoxicillin- and clavulanic acid-specific T cells in patients with Amoxicillin-clavulanate-induced liver injury. Hepatology 62(3):887-899 PMID 25998949 Ogese MO (2017) Characterization of drug-specific signaling between primary human hepatocytes and immune Cells. Toxicol Sci. 158(1):76-89 PMID 28444390 Pitout JD, Sanders CC, Sanders WE (1997) Antimicrobial resistance with focus on beta-lactam resistance in gram-negative bacilli. Am J Med 103(1):51-59. PMID 9236486 Reading C and Cole M (1977) Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhibiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 11(5):852-857 PMID 879738 Worlitzch D et al (2001) Effects of Amoxicillin, gentamicin, and moxifloxacin on the hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45(1):196-202 PMID 11120965 |
| MIC | Agrobacterium radiobacter| 0.25 - 16|| Alcaligenes faecalis| 8 - 64|| Bacillus circulans| ≤0.015 - 2|| Bacteroides capillosus | ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Bacteroides merdae| 0.016 - 0.5|| Bacteroides ovatus| 0.016 - 0.5|| Bacteroides ureolyticus| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Bifidobacterium adolescentis| 0.016 - 0.5|| Bifidobacterium breve| ≤0.015 - 2|| Bifidobacterium longum| ≤0.015 - 2|| Bifidobacterium sp.| 0.016 - 0.5|| Bordetella bronchiseptica| 8 - 64|| Brevundimonas vesicularis| 4 - >64|| Burkholderia cepacia| >64|| Campylobacter coli| 0.5 - 16|| Campylobacter concisus| 0.06 - >8|| Campylobacter gracilis| 0.06 - >8|| Campylobacter jejuni| 0.12 - 16|| Campylobacter mucosalis| 0.06 - >8|| Campylobacter rectus| 0.06 - >8|| Campylobacter showae| 0.06 - >8|| Campylobacter sputorum| 0.06 - >8|| Capnocytophaga ochracea | ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Capnocytophaga spp.| 0.016 - 64|| Chryseobacterium indologenes| 0.5 - >64|| Chryseobacterium meningosepticum| 32 - >64|| Collinsella aerofaciens| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Comamonas acidovorans| 32 - >64|| Corynebacterium jeikeium| 1 - >8|| Dialister pneumosintes | ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Edwardsiella hoshinae | 0.06 - 0.25|| Edwardsiella ictaluri | 0.06 - 1|| Edwardsiella tarda| 0.06 - 4|| Eikenella corrodens| 0.25 - 2|| Enterococcus faecalis| 0.016 - 64|| Enterococcus faecium| 0.5 - >256|| Escherichia coli| 0.016 - 512|| Eubacterium lentum| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Eubacterium saburreum| ≤0.015 - 0.125|| Eubacterium spp.| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Eubacterium timidum| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Eubacterium yurii| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Finegoldia magna| ≤0.015 - 2|| Fusobacterium naviforme| ≤0.015 - 0.5|| Fusobacterium necrophorum| ≤0.015 - 0.5|| Fusobacterium nucleatum| ≤0.015 - 0.5|| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.016 - 0.5|| Gemella morbillorum| 0.016 - 64|| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.016 - 64|| Haemophilus parainfluenzae| 0.016 - 64|| Haemophilus spp.| 0.75 - 2|| Helicobacter pylori| <0.01 - 0.02|| Hemolytic streptococci (group C)| 0.016 - 0.25|| Hemolytic streptococci (group G)| 0.016 - 0.25|| Lactobacillus catenaforme| ≤0.015 - 2|| Lactobacillus delbrueckii| ≤0.015 - 2|| Lactobacillus oris| ≤0.015 - 2|| Lactobacillus plantarum| ≤0.015 - 2|| Lactobacillus spp.| ≤0.015 - 2|| Leptotrichia buccalis| ≤0.015 - 0.5|| Micromonas micros| 0.06 - 4|| Moraxella catarrhalis| ≤0.008 - 64|| Neisseria cinerea| 0.5 - 2|| Neisseria elongata | 0.5 - 2|| Neisseria meningitidis| ≤0.06 - 0.5|| Neisseria sicca| 0.5 - 2|| Neisseria spp.| 0.5 - 2|| Nocardia brasiliensis| 1 - 32|| Ochrobactrum anthropi| 32 - ≥128|| Oligella ureolytica| 0.25 - >64|| Olsenella uli| ≤0.015 - 2|| Parvimonas micra| 0.016 - 0.75|| Pasteurella haemolytica| ≤1 - 0.5|| Peptoniphilus gorbachii | 0.016 - 0.064|| Peptoniphilus harei | 0.016 - 0.38|| Peptoniphilus ivorii | 0.016 - 0.032|| Peptoniphilus lacrimalis | 0.016 - 0.25|| Peptoniphilus octavius | 0.064|| Peptostreptococcus anaerobius| ≤0.015 - 4|| Porphyromonas endodontalis | ≤0.015 - 0.5|| Porphyromonas gingivalis| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Prevotella buccae| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella buccalis| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella corporis | ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella dentalis | ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella denticola| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella disiens| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella intermedia| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella loescheii| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella melaninogenica| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella nigrescens| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella oralis| 0.016 - 1|| Prevotella oris| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella pallens | ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella spp.| ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella tannerae | ≤0.015 - 1|| Prevotella zooglioformans | ≤0.015 - 1|| Propionibacterium avidum| ≤0.015 - 2|| Propionibacterium sp. | 0.016 - 0.5|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| >64 - >512|| Pseudomonas oryzihabitans| 2|| Pseudomonas stutzeri| 0.25 - 16|| Ralstonia pickettii | 1 - >64|| Rothia dentocariosa| 0.016 - 64|| Rothia mucilaginosa| 0.016 - 64|| Ruminococcus gnavus| 0.19|| Selenomonas flueggei | ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Selenomonas infelix | ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Selenomonas spp.| ≤0.015 - 0.25|| Sphingomonas spp.| 8 - 32|| Staphylococci| 0.03 - 64|| Staphylococcus aureus| 0.016 - 64|| Staphylococcus epidermidis| 0.016 - 64|| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia| 8 - >64|| Streptococci| 0.03 - 0.25|| Streptococcus acidominimus | 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus agalactiae| 0.03 - 0.25|| Streptococcus anginosus| 0.016 - 0.25|| Streptococcus bovis| ≤0.06 - 0.12|| Streptococcus constellatus| 0.016 - 0.25|| Streptococcus intermedius| 0.016 - 0.25|| Streptococcus mitis| 0.016 - 1|| Streptococcus oralis| 0.016 - 1|| Streptococcus ovis | 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus parasanguinis | 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus pluranimalium | 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus pneumonia| ≤0.008 - 16|| Streptococcus pyogenes| 0.03 - 0.25|| Streptococcus salivarius| 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus sanguinis| 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus sobrinus| 0.016 - 0.5|| Streptococcus spp| ≤0.06 - >8|| Streptococcus thoraltensis | 0.016 - 0.5|| Veillonella spp.| 0.06 - 4|| Weeksella virosa | ≤0.06 - 0.5|| |