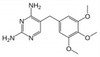
Trimethoprim is a synthetic derivative of trimethoxybenzyl-pyrimidine with bacteriostatic and antiprotozoal properties. As a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, trimethoprim binds tightly to the bacterial enzyme, blocking the production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid, arresting folic acid synthesis.
When Trimethroprim is combined with sulfonamides, like Sulfamethoxazole (S045), the two compounds show bactericidal effects, but are only bacteriostatic when used separately. The activity is attributed to their synergistic effect in inhibiting folic acid metabolism in bacteria.
Trimethoprim has a wide antibacterial spectrum and is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, including Nocardia, Brucella, Gram-negative bacilli, and some Gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus, Toxoplasma and some other coccidians. It is used to treat recurrent cystitis, mild acute prostatitis, urinary tract infections, asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy and respiratory tract infections. The product is very slightly soluble in aqueous solution.
We also offer:
- Trimethoprim Lactate (T012)
| Mechanism of Action | Trimethoprim interferes with the cellular metabolism of folic acid in the bacterial cell by blocking the biosynthesis of nucleotides. Trimethoprim binds to dihydrofolate reductase and inhibits the reduction of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid. Tetrahydrofolic acid is an essential precursor in the thymidine synthesis pathway and interference with this pathway inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis. |
| Spectrum | Trimethoprim has a wide antibacterial spectrum and is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic bacteria, including Nocardia, Brucella, Gram-negative bacilli, and some Gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus, Toxoplasma and some other coccidians. It is used to treat recurrent cystitis, mild acute prostatitis, urinary tract infections, asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy and respiratory tract infections. |
| Microbiology Applications | Trimethoprim is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
Media SupplementTrimethoprim can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media: Columbia Blood Agar - Campylobacter selective supplement (Skirrow) Columbia Blood Agar - Campylobacter selective supplement (Blaser-Wang) Campylobacter Agar - Campylobacter Selective Supplement (Preston) Columbia Blood Agar - Helicobacter pylori Selective Supplement (Dent) Bolton Broth - Bolton Broth Selective Supplement Campylobacter Agar Base - Modified Preston Campylobacter Selective Supplement Bolton Broth - Modified Bolton Broth Selective Supplement ChromogenicBacillus cereus Agar - Chromogenic Bacillus cereus Selective Supplement |
| Plant Biology Applications | Trimethoprim can be used in combination with rifampicin to provide sufficient coverage against pathogenic microbes. When used without other supplemental antibiotics, Trimethoprim was not shown to provide sufficient coverage (Pollock et al, 1983). |
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N4O3 |
| Impurity Profile | Chromotographic Purity: Individual Impurity: ≤0.1%; Total Impurities: ≤0.2% |
| References |
Weir DG and Scott J (2000) Mechanism of the antimicrobial drug Trimethoprim revisited. Journal vol (issue):2519-2524 |
| MIC | Aeromonas spp.| 128 - ?| 478| Bacteroides fragilis (NCTC 9343)| 16 - ?| 401| Burkholderia cenocepacia (K56-2)| 4 - ?| 951| Burkholderia cepacia (CEP509)| 4 - ?| 951| Burkholderia multivorans (ATCC 17616)| 4 - ?| 951| Burkholderia stabilis (LMG 14086)| 2 - ?| 951| Burkholderia vietnamensis (16232)| 2 - ?| 951| Campylobacter jejuni| ? - ?| 62| Campylobacter jejuni| ? - ?| 491| Campylobacter spp.| 64 - ?| 478| Citrobacter freundii| 19.5 - ?| 27| Edwardsiella tarda| 312.5 - ?| 27| Enterobacter| 156.2 - ?| 27| Enterobacteriaceae| 0.03 - 128| 401| Enterococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212)| 0.25 - ?| 401| Enterococcus faecalis (G + ve)| 78.1 - ?| 27| Enterococcus faecium (ACA-DC 3350)| 256 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (ACA-DC 3359)| 256 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (PCD 71)| 256 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (PCK 38)| 256 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (PCK 45)| 256 - ?| 910| Escherichia coli| ≤0.062 - >512| 436| Escherichia coli| 0.25 - 64| 873| Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922)| 0.25 - ?| 401| Escherichia coli (chicken isolate)| ? - ?| 1037| Escherichia coli (enteroaggregative)| ? - ?| 62| Escherichia coli (enteroaggregative)| ? - ?| 491| Escherichia coli (enteroaggregative)| 1024 - ?| 478| Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic)| ? - ?| 491| Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic)| ? - ?| 62| Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic)| 1024 - ?| 478| Escherichia coli (isolate 1)| 1 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 2)| 1 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 3)| 128 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 4)| 64 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 5)| 32 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 6)| 8 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (isolate 7)| 128 - ?| 849| Escherichia coli (NCTC 10418)| 0.12 - ?| 401| Escherichia coli (NCTC 10418)| 19.5 - ?| 27| Escherichia coli (swine isolate)| ? - ?| 1037| Escherichia coli (XL2)| 0.5 - ?| 393| Escherichia coli (XL2)| 0.5 - ?| 622| Escherichia coli (XL2-66-6976-1)| 0.5 - ?| 622| Escherichia coli (XL2-66-6976-1)| 0.5 - ?| 393| Escherichia coli (XL2-66-6976-2)| 1 - ?| 393| Escherichia coli (XL2-66-6976-2)| 1 - ?| 622| Haemophilus influenzae (ATCC 31517)| 0.25 - ?| 88| Haemophilus influenzae (trimethoprim-resistant)| ≥16 - ?| 452| Haemophilus influenzae (trimethoprim-susceptible)| ≤8 - ?| 452| Haemophilus influenzae (VHIN6529)| 1 - ?| 88| Haemophilus influenzae (VHIN6536)| 0.5 - ?| 88| Haemophilus spp.| 0.15 - 16| 401| Klebsiella pneumonia| 5000 - ?| 27| Klebsiella pneumonia (G340)| 2 - ?| 174| Klebsiella pneumonia (G595)| 0.5 - ?| 174| Klebsiella pneumonia (GC 7535)| 0.25 - ?| 174| Klebsiella pneumonia (GC 7736)| 16 - ?| 174| Klebsiella pneumonia (GC 7737)| 16 - ?| 174| Klebsiella pneumonia (GC 7737)| 16 - ?| 174| Lactobacillus acidophilus| 2 - 64| 1036| Lactobacillus buchneri| 0.5 - 128| 1036| Lactobacillus pentosus (PCD 101)| 256 - ?| 910| Lactobacillus plantarum| ≤0.125 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus reuteri| 0.25 - >=256| 1036| Lactobacillus salivarius| 0.25 - 64| 1036| Lactococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Leuconostoc| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Leuconostoc mesenteroides (PCD 119)| 256 - ?| 910| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides (PCK 18)| 64 - ?| 910| Morganella morganii| 156.2 - ?| 27| Nocardia asteroides| 3.1 - >=200| 1404| Pediococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Pediococcus pentosaceus (PCD 215)| 256 - ?| 910| Pediococcus pentosaceus (PCD 237)| 256 - ?| 910| Plesiomonas shigelloides| 4.9 - ?| 27| Plesiomonas shigelloides| 128 - ?| 478| Proteus morganii| 156.2 - ?| 27| Proteus rettgeri| 2500 - ?| 27| Proteus vulgaris| 156.2 - ?| 27| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 5000 - ?| 27| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 15692)| 32 - ?| 786| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (DB5218)| 32 - ?| 786| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (DR3062)| 32 - ?| 786| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NCTC 10662)| 32 - ?| 401| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA01)| 32 - ?| 786| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PT121)| 32 - ?| 786| Salmonella enteritidis| 4.9 - ?| 27| Salmonella Paratyphi (B)| 9.8 - ?| 27| Salmonella Paratyphi (B)| 156.2 - ?| 27| Salmonella spp.| ? - ?| 62| Salmonella spp.| ? - ?| 491| Salmonella spp.| 1024 - ?| 478| Salmonella typhi| 4.9 - ?| 27| Salmonella typhimurium| 5000 - ?| 27| Shigella boydii| 9.8 - ?| 27| Shigella flexneri| ? - ?| 62| Shigella flexneri| ? - ?| 491| Shigella flexneri| 156.2 - ?| 27| Shigella sonnei| ? - ?| 491| Shigella sonnei| ? - ?| 62| Shigella sonnei| 9.8 - ?| 27| Shigella spp.| 1024 - ?| 478| Staphylococci| 0.03 - 8| 401| Staphylococcus albus (G + ve)| >5000 - ?| 27| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213)| 0.5 - ?| 401| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6571)| 0.25 - ?| 401| Staphylococcus aureus (G + ve)| >5000 - ?| 27| Staphylococcus aureus (JSB20013)| 1 - ?| 748| Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-resistant)| ? - ?| 452| Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible)| ? - ?| 452| Staphylococcus aureus (RN1024-tms)| 2 - ?| 601| Staphylococcus aureus (RN4220 + pVGA)| 2 - ?| 601| Staphylococcus aureus (RN4220)| 2 - ?| 601| Staphylococcus aureus (RN4220/tet(A)/pYH4)| 1 - ?| 748| Staphylococcus aureus (trimethoprim-resistant)| ≥16 - ?| 452| Staphylococcus aureus (trimethoprim-susceptible)| ≤8 - ?| 452| Streptococcus bovis| 0.5 - 16| 1036| Streptococcus equi subsp. equi (2002–2006)| ? - ?| 937| Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (2002–2006)| ? - ?| 937| Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (2007–2008)| ? - ?| 937| Streptococcus infantarius| 0.5 - 16| 1036| Streptococcus pneumonia (ATCC 49219)| 4 - ?| 88| Streptococcus pneumonia (ATCC 49619)| 4 - ?| 401| Streptococcus pneumonia (Duke-2)| 8 - ?| 918| Streptococcus pneumonia (trimethoprim-resistant)| ≥16 - ?| 452| Streptococcus pneumonia (trimethoprim-susceptible)| ≤8 - ?| 452| Streptococcus pneumonia (VSPN6521)| 4 - ?| 88| Streptococcus pneumonia (VSPN6522)| 2 - ?| 88| Vibrio cholerae (0139)| 39.1 - ?| 27| Vibrio cholerae (1)| 5000 - ?| 27| Vibrio cholerae (non-01)| 1.2 - ?| 27| Vibrio harveyi| 6.25 - ?| 1428| Vibrio harveyi| >25 - ?| 1428| Weissella spp.| 1 - >=256| 1036| Xanthomonas campestris pv. mangiferaeindicae (Xm)| 16 - 64| 1432| Yersinia enterocolitica| ? - ?| 62| Yersinia enterocolitica| ? - ?| 491| |