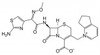
Cefpirome Sulfate Solubilized is a mixture of Cefpirome Sulfate with anhydrous sodium carbonate that is used to stabilize the pH in aqueous solution. Cefpirome Sulfate is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, fourth generation cephalosporin antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, and is resistant to β-lactamases. Cefpirome Sulfate is susceptible to degradation in aqueous solutions and optimal stability is pH 4-6. Cefpirome Sulfate Solubilized is soluble in water.
We also offer:
- Cefpirome Sulfate (C014)
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. The relative lack of cross-resistance between Cefpirome and the third-generation cephalosporins suggests a slightly different mechanism of action of Cefpirome in comparison to the other cephalosporins. Due to its compact dipolar structure, Cefpirome can penetrate Gram-negative bacteria more quickly than the other agents (Nikaido et al, 1990). |
| Spectrum | Cefpirome is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Many Bacteroides, Enterococci, and Haemophilus species have developed resistance to Cefpirome. |
| Microbiology Applications | Cefpirome is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options . Representative effective ranges include:
|
| Cancer Applications | Cefpirome was found to be more effective than ceftazidime, aztreonam, timentin, and piperacillin against nosocomially important isolates during in vitro examination of 253 bacterial isolates (Rolston et al, 1986). |
| Molecular Formula | C22H22N6O5S2·H2SO4 (Cefpirome Sulfate) |
| Assay | (On Dried Basis): 80.3-89.2% (content of Cefpirome Sulfate) |
| References | Hafeez S, Izhar M, Ahmed A, Zafar A, and Naeem M (2000) In vitro antimicrobial activity of Cefpirome: A new fourth-generation cephalosporin against clinically significant bacteria. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 50(8):250-252 PMID 10992706 Kobayashi S, Arai S, Hayashi S and Fujimoto K (1986) β-Lactamase Stability of Cefpirome (HR 810), a new cephalosporin with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 30(5):713-718 PMID 3492175 Nikaido H, Liu W and Rosenberg EY (1990) Outer membrane permeability and beta-lactamase stability of dipolar ionic cephalosporins containing methoxyimino substituents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34(2):337-342 PMID 2109581 Rolston KVI, Alvarez ME, Hsu K, and Bodey GP (1986) In-vitro activity of Cefpirome (HR-810), WIN-49375, BMY-28142 and other antibiotics against nosocomially important isolates from cancer patients, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 17(4):453–457 Rolston K et al (1986) Comparative in vitro activity of Cefpirome and other antimicrobial agents against isolates from cancer patients. Chemother. 32(4):344-351 Zalewski P et al (2016) Stability of Cefpirome Sulfate in aqueous solutions. Acta Poloneae Pharma- Drug Res. 73(1):23-27 |
| MIC | Acinetobacter anitratus| 1 - 128 | Acinetobacter calcoaeeticus| 8 - >64 | Aeromonas spp.| 0.015 - 2 | Bacteroides distasonis| 16 - >32 | Bacteroides fragilis| 4 - 128 | Bacteroides melaninogenicus| 16 - >32 | Bacteroides ovatus| 16 - >32 | Bacteroides septicum| 16 - >32 | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 16 - >32 | Bordetella pertussis | 0.25 - 0.5 | Burkholderia cepacia| 16 - >128 | Campylobacter jejuni| 0.5 - 8 | Citrobacter diversus| 0.015 - 0.03 | Citrobacter freundii| 0.03 - >16 | Clostridium perfringens| 0.25 - >16 | Enterobacter aerogenes| 0.03 - 1 | Enterobacter cloacae| 0.013 - 100 | Enterobacteriaceae| 0.008 - 32 | Enterococci| 1 - 128 | Enterococcus faecalis| 2 - 128 | Enterococcus faecium| 1 - >128 | Escherichia coli| 0.013 - 2 | Haemolytic streptococci| 0.004 - 0.12 | Haemophilus influenzae| 0.03 - 0.5 | Haemophilus spp.| 0.008 - 0.5 | Klebsiella aerogenes| 0.025| Klebsiella oxytoca| 0.03 - 1 | Klebsiella pneumonia| 0.03 - 256 | Klebsiella pneumonia| 0.032 - 0.5 | Klebsiella spp.| 0.015 - 2 | Listeria monocytogenes| 1 - 32| Moraxella catarrhalis| 0.03 - 4 | Morganella morganii| 0.03 - 0.5 | Neisseria spp.| 0.001 - 0.12 | Pasteurella multocida| <8 | Pneumococci| 0.008 - 1 | Proteus mirabilis| 0.015 - 0.5 | Proteus vulgaris| 0.03 - 8 | Providencia rettgeri| 0.008 - 8 | Providencia stuartii| 0.03 - 0.5 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 0.0781 - >128 | Pseudomonas cepacia| 0.12 - >64 | Pseudomonas spp.| 0.25 - 128 | Salmonella spp.| 0.015 - 3 | Salmonella typhimurium| 0.015 - 0.12 | Serratia marcescens| 0.03 - >100 | Shigella sonnei| 0.015 - 0.25 | Shigella spp.| 0.015 - 0.5 | Staphylococcus spp.| 0.06 - 128 | Staphylococcus aureus| 0.098 - 64 | Staphylococcus epidermidis| 0.125 - 64 | Staphylococcus saprophyticus| 0.5 - 16 | Streptococci| 0.015 - 0.25 | Streptococcus agalactiae| 0.03 - 0.063 | Streptococcus pneumoniae| 0.008 - 2 | Streptococcus pneumoniae| 0.015| Streptococcus pneumoniae| 0.015| Streptococcus pyogenes| 0.007 - 1.563 | Xanthomonas maltophilia| 4 - >64 | Yersinia enterocolitica| 0.015 - 3 | |