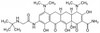
Tigecycline is a broad spectrum glycylcycline antibiotic with activity against multi-drug resistant organisms. It is a semisynthetic derivative of tetracycline, that is structurally similar to minocycline; however, it contains a large glycylamido group at the D-9 position. This substitution is thought to be the reason behind its broad-spectrum activity.
Tigecycline is a protein synthesis inhibitor with bacteriostatic activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It was designed be less affected by the two major tetracycline-resistance mechanisms, ribosomal protection and efflux and was approved by the FDA in 2005. Additionally, Tigecycline is not affected by resistance mechanisms such as β-lactamases (including extended spectrum β-lactamases), target-site modifications, macrolide efflux pumps or enzyme target changes (e.g. gyrase/topoisomerases). However, some ESBL-producing isolates may confer resistance to Tigecycline via other resistance mechanisms. Tigecycline resistance in some bacteria (e.g. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex) is associated with multi-drug resistant (MDR) efflux pumps.
Tigecycline has recently shown anti-tumor properties and is being evaluated for Tigecycline’s inhibitory effects on several activating signaling pathways and abnormal mitochondrial function in cancer cells.
Tigecycline is soluble in DMSO and DMF. Very slighty soluble in water.
This product is considered a dangerous good. Quantities above 1 g may be subject to additional shipping fees. Please contact us for specific questions.